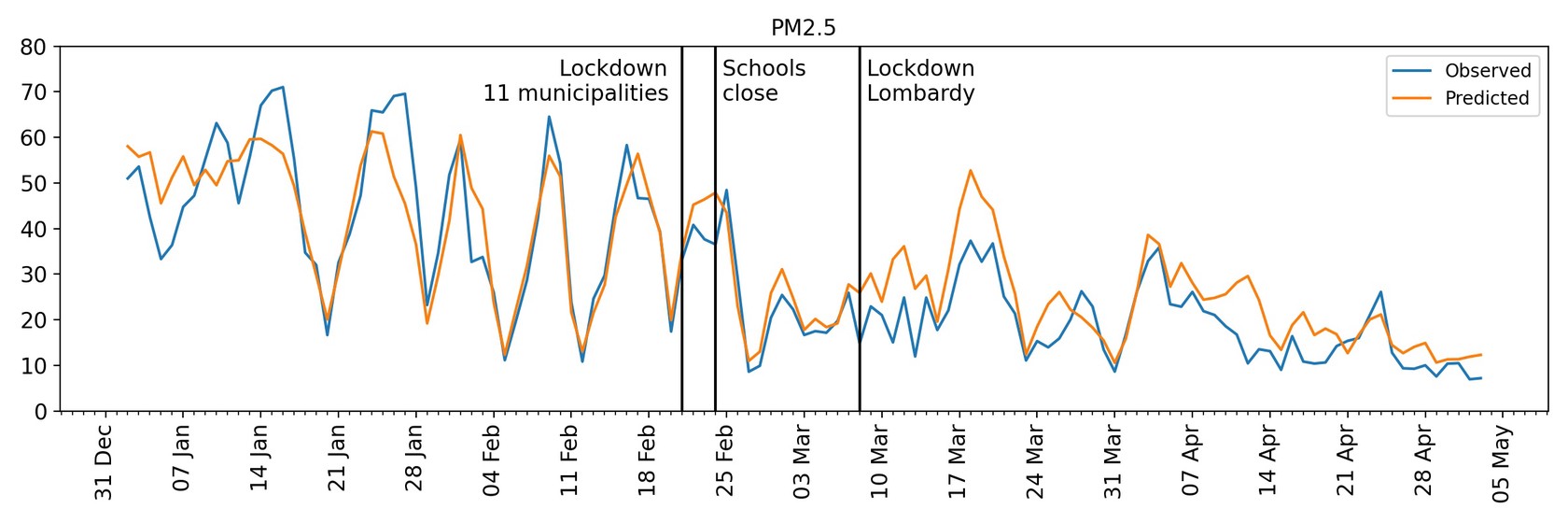

Evaluating the reduction in pollution caused by a sudden change in emissions is complicated by the confounding effect of weather variations. We propose an approach based on machine learning to build counterfactual scenarios that address the effect of weather and apply it to the COVID-19 lockdown of Lombardy, Italy. We show that the lockdown reduced background concentrations of PM2.5 by 3.84 µg m−3 (16%) and NO2 by 10.85 µg m−3 (33%). Improvement in air quality saved at least 11% of the years of life lost and 19% of the premature deaths attributable to COVID-19 in the region during the same period. The analysis highlights the benefits of improving air quality and the need for an integrated policy response addressing the full diversity of emission sources.
Published on Environmental Research Letters.
With Lara Aleluis Reis, Valentina Bosetti, and Massimo Tavoni.
Evaluating the reduction in pollution caused by a sudden change in emissions is complicated by the confounding effect of weather variations. We propose an approach based on machine learning to build counterfactual scenarios that address the effect of weather and apply it to the COVID-19 lockdown of Lombardy, Italy. We show that the lockdown reduced background concentrations of PM2.5 by 3.84 µg m−3 (16%) and NO2 by 10.85 µg m−3 (33%). Improvement in air quality saved at least 11% of the years of life lost and 19% of the premature deaths attributable to COVID-19 in the region during the same period. The analysis highlights the benefits of improving air quality and the need for an integrated policy response addressing the full diversity of emission sources.